Thyroid
Understanding Thyroid Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
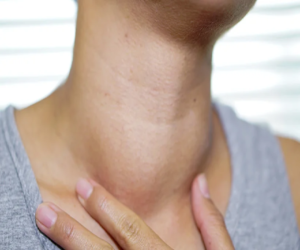
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall body functions. Thyroid disorders occur when the gland produces too much or too little hormone, leading to various health issues.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders are mainly classified into:
-
-
Hypothyroidism: A condition where the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones, slowing down bodily functions.
-
-
-
Hyperthyroidism: Overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to an increased metabolic rate.
-
-
-
Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, often due to iodine deficiency.
-
-
-
Thyroid Nodules: Lumps in the thyroid gland, which can be benign or cancerous.
-
-
-
Thyroid Cancer: A rare but serious condition that affects the thyroid cells.
-
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to thyroid disorders, including:
-
-
Iodine Deficiency: Essential for thyroid hormone production, lack of iodine can lead to goiter and hypothyroidism.
-
-
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease cause thyroid dysfunction.
-
-
-
Genetics: A family history of thyroid disorders increases the risk.
-
-
-
Hormonal Imbalances: Pregnancy and menopause can trigger thyroid issues.
-
-
-
Medications and Radiation Exposure: Certain drugs and radiation therapy may affect thyroid function.
-
Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
The symptoms vary depending on the type of thyroid disorder:
-
-
Hypothyroidism: Fatigue, weight gain, depression, dry skin, hair loss, slow heart rate, and cold intolerance.
-
-
-
Hyperthyroidism: Weight loss, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, sweating, irritability, and heat intolerance.
-
-
-
Goiter and Nodules: Swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or breathing problems.
-
