Psorasis
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes rapid skin cell growth, leading to scaling, inflammation, and redness. It affects millions of people worldwide and can impact not only the skin but also overall well-being. While there is no permanent cure, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis appears in different forms, each with unique symptoms:
-
-
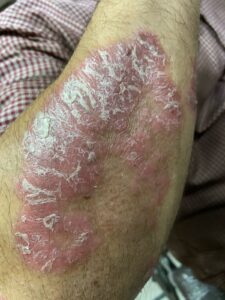
Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris) – The most common type, causing red, inflamed patches with silvery-white scales on the skin.
-
-
-
Guttate Psoriasis – Small, red, drop-like lesions, often triggered by infections like strep throat.
-
-
-
Inverse Psoriasis – Red, shiny lesions in skin folds (e.g., armpits, under the breasts, and around the groin).
-
-
-
Pustular Psoriasis – White pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin, often occurring on the hands and feet.
-
-
-
Erythrodermic Psoriasis – A severe, life-threatening form that causes widespread redness, peeling, and extreme pain.
-
Causes and Risk Factors
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This leads to faster-than-normal skin cell turnover (every few days instead of weeks), resulting in skin buildup.
Common Triggers of Psoriasis:
-
-
Genetics – A family history of psoriasis increases the risk.
-
-
-
Immune System Dysfunction – Overactive T-cells cause inflammation.
-
-
-
Infections – Bacterial or viral infections can trigger flare-ups.
-
-
-
Stress – Emotional and physical stress may worsen symptoms.
-
-
-
Weather Changes – Cold, dry weather can aggravate psoriasis.
-
-
-
Skin Injuries – Cuts, burns, or bug bites may trigger a flare-up (Koebner phenomenon).
-
-
-
Certain Medications – Beta-blockers, lithium, and some anti-inflammatory drugs can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
-

 Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
