Uric Acid
Understanding Uric Acid: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Uric acid is a waste product formed from the breakdown of purines, which are found in certain foods and body cells. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is eliminated through the kidneys. However, excessive uric acid levels can lead to health complications such as gout and kidney stones.
Causes of High Uric Acid Levels
Several factors contribute to elevated uric acid levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming purine-rich foods like red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks can increase uric acid.
- Obesity: Excess weight can reduce the body’s ability to eliminate uric acid efficiently.
- Kidney Issues: Impaired kidney function can lead to the accumulation of uric acid.
- Genetics: A family history of gout or high uric acid levels increases the risk.
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes, high blood pressure, and metabolic disorders can contribute to increased uric acid.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol, especially beer and liquor, can raise uric acid levels.
Symptoms and Complications
High uric acid levels may not always cause symptoms, but when they do, they can lead to:
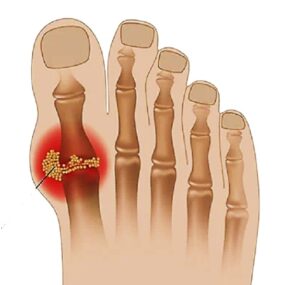
- Gout: Severe joint pain, redness, and swelling, often in the big toe.
- Kidney Stones: Formation of uric acid crystals in the kidneys, leading to pain and urinary issues.
- Joint Damage: Chronic high levels can result in long-term joint deformities.
Management and Prevention
Managing uric acid levels involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Effective strategies include:
- Healthy Diet: Avoiding purine-rich foods and increasing water intake to flush out uric acid.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight helps improve uric acid metabolism.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activities helps maintain overall health.
- Limiting Alcohol: Reducing alcohol intake can lower uric acid levels.
- Medications: In severe cases, doctors may prescribe medications like allopurinol to control uric acid production.
Conclusion
Monitoring and managing uric acid levels is essential for preventing gout and kidney-related issues. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and medical guidance can help maintain healthy levels. If uric acid levels remain high despite lifestyle changes, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for proper treatment.
