Cholestrol
Understanding Cholesterol: Types, Risks, and Management
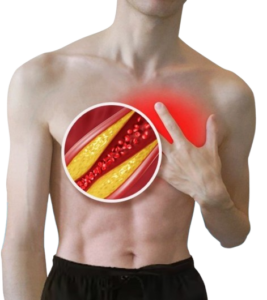
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the blood that is essential for building healthy cells. However, excessive cholesterol levels can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease. It is produced by the liver and also obtained from certain foods.
Types of Cholesterol
Cholesterol is classified into two main types:
-
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Known as ‘bad’ cholesterol, high levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
-
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Referred to as ‘good’ cholesterol, HDL helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to high cholesterol levels, including:
-
Unhealthy Diet: Consuming foods high in saturated and trans fats can increase LDL cholesterol.
-
Lack of Exercise: Physical inactivity can lower HDL levels and contribute to weight gain.
-
Genetics: A family history of high cholesterol can make an individual more prone to the condition.
-
Obesity: Excess weight is linked to higher LDL and lower HDL levels.
-
Smoking: Smoking reduces HDL cholesterol and damages blood vessels.
-
Medical Conditions: Diabetes, hypertension, and liver disease can contribute to high cholesterol.
Symptoms and Complications
High cholesterol itself does not cause symptoms, making regular checkups crucial. If left untreated, it can lead to:
-
Atherosclerosis (narrowed arteries)
-
Heart attack
-
Stroke
-
High blood pressure
Management and Prevention
Managing cholesterol involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Some effective strategies include:
-
Healthy Diet: Eating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while avoiding fried and processed foods.
-
Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of high cholesterol.
-
Quitting Smoking: Stopping smoking improves HDL levels and overall heart health.
-
Medications: Statins and other prescribed drugs may be recommended for individuals with high cholesterol levels.
